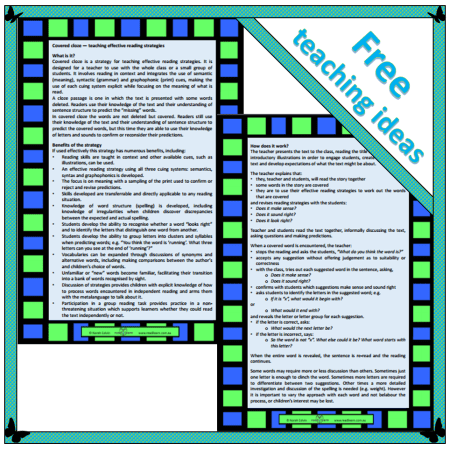
This week at the Carrot Ranch, Charli Mills challenged writers to In 99 words (no more, no less) write a story that is a sketch or about a sketch. It can be “A Sketch of a Romance” or “The Sketch of Aunt Tillie.” Go where the prompt leads you to scribble.
My thoughts were a bit sketchy. This is what I came up with. I’d be interested to know your perception.
Sketchy Perceptions
He sketched the outline with chalk then filled in the details, outside-in. Curious passers-by gathered as the image emerged. Was the artist a paid entertainer or busker earning a buck? Some pushed coins into children’s hands to add to the chalk-drawn cap. When satisfied with his work, the artist stood in its centre and tossed the cap and contents high. As they fell, he spread his arms and disappeared into the painting. Perplexed on-lookers reported different perceptions. Many said he plummeted into darkness. Some said he flew on gold-tipped wings. Others described him simply as absorbed by his art.

It is easy to make snap judgements about others and situations from sketchy information, even at first sight. We do it all the time as we try to make sense of what we perceive, evaluating it against our existing knowledge and beliefs.
I have strong beliefs about education and how children learn so can quickly judge whether I will agree with the content of articles or not. However, I don’t confine my reading to articles that I know will support my beliefs. I read articles from a variety of viewpoints to gain some understanding of others’ positions. If I don’t know what they think, how can I interrogate those thoughts and evaluate them against my own, perhaps even reassess my beliefs? I would rather be informed than base my ideas upon sketchy information.
This week, I had the pleasure of reading two articles in popular media which reiterate things I have written about a number of times previously.
The title of an article by Angela Mollard in my local Courier-Mail intrigued me: We should be ashamed of how we treat teachers. The media is often quick to criticise teachers, blaming them for almost all of society’s ills, it sometimes seems. I wondered at the intent of this article. Mollard wrote that, although she is the daughter of a teacher, sister-in-law of a teacher, and friends with many teachers, she had no idea of a teacher’s life until she read the book Teacher by Gabbie Stroud. I am yet to read this memoir, but it is now high on my TBR list.
Mollard says, “She (Stroud) writes of the sacred bond between teacher and pupil, of advocating exhaustively for their needs, of loving them even when they were abusive and damaged and victims of the most heartbreaking of family circumstances.”
Mollard follows this by telling us that “Ultimately, Stroud gives up being a teacher. She’s broken by the profession but she maintains that she didn’t leave teaching, it left her”, and describes her book as “a clarion call to educators to change a system that values standardisation over creativity, curiosity, progress, self-belief and autonomy.”
Oh, yes! I applaud. I know many teachers who feel the same way.
Mollard then goes on to say that if parents want inspirational teachers for their children, they must be inspirational too, that they must stand beside and support teachers and do what they can to lighten their workload so more help can be given where it is truly needed. If you are a parent, please read the article for her suggestions. I have sketched out just a few of her ideas here.
If you can do only one thing for your children, it should be shared reading is the title of an article by Ameneh Shahaeian and Cen Wang in The Conversation. To any regular readers of my blog, the idea behind the title will be very familiar. It gladdens me when I see others promoting such good advice for parents.
However, in the article Shahaeian and Wang surprised me with the question, “is it really book reading that’s beneficial or is it because parents who read more to their children also provide a lot of other resources, and engage in a range of other activities with their children?”
Does the question intrigue you as much as it did me? Shahaeian and Wang share the results of a longitudinal study they carried out to find an answer. Please read the article for their conclusions and suggestions for parents.
I’ve provided you with just the sketchy outlines of both these articles. If you are interested enough to read them, I’d love to know what you think.

Thank you for reading. I appreciate your feedback. Please share your thoughts.

 Continue reading: readilearn: Interactive whiteboard resources for kindergarten
Continue reading: readilearn: Interactive whiteboard resources for kindergarten